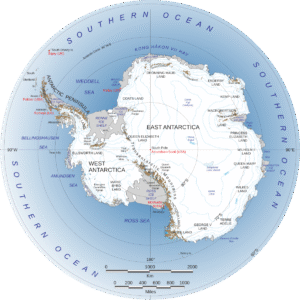
Antarctica is Earth’s southernmost continent, containing the geographic South Pole. It is a vast, remote, and icy landmass known for its extreme climate, unique ecosystems, and critical importance to global science and climate research.
Key Facts About Antarctica:
-
Location: Southern Hemisphere, surrounding the South Pole.
-
Size: Approximately 14 million square kilometers (5.4 million square miles), making it the fifth-largest continent.
-
Climate: Coldest, driest, and windiest continent on Earth. Temperatures can drop below -80°C (-112°F) in the winter.
-
Ice Coverage: About 98% of Antarctica is covered by ice, which holds around 60% of the world’s fresh water.
-
Population: No permanent residents. Hosts around 1,000 to 5,000 temporary researchers and scientists at various research stations throughout the year.
-
Wildlife: Despite harsh conditions, it’s home to species like penguins, seals, krill, and various seabirds. There are no land mammals or native human populations.
-
Governance: Governed by the Antarctic Treaty System (signed in 1959), which prohibits military activity, mineral mining, and supports scientific cooperation.
-
Importance: Antarctica plays a major role in regulating Earth’s climate and ocean currents. Its ice sheets are crucial indicators of climate change.